Open your wallet right now. Most likely, you have a debit card, a credit card, a health insurance card, and access to the massive financial infrastructure that these three cards represent.
The ability to store, save, use, and borrow money anywhere in almost limitless fashion, without worry about amount, theft, or even making change. Add in the freedom from a direct worry about health costs, and these three cards represent a level of financial freedom unknown to anyone in the developing world… today.
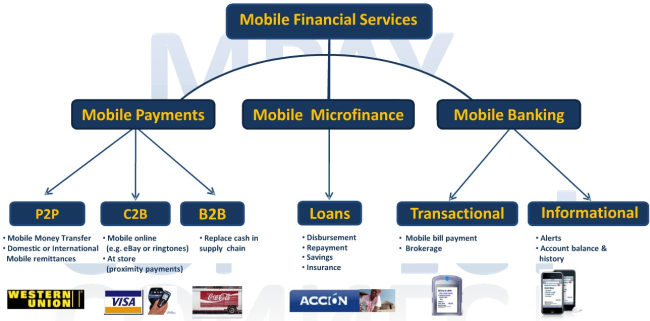
Mobile Money Revolution
Yet by tomorrow, there will be more people who have similar access to financial services, via electronic transactions on mobile phones. In fact, over the next five years there will be a mobile money revolution at the bottom of the pyramid as international financial institutions like VISA, Mastercard, and the like move in forcefully to service the next billion customers.
They see M-PESA transferring 20% of Kenya’s GDP and the money that can be made offering mobile financial services to the BoP. But its not just payments and credit, there are also opportunities in many other types of financial services.
Here are two examples with insurance, which is usually the providence of in-person sales worldwide:
Now we could go on, but listing examples of mobile money was not the focus of the Technology Salon on how mobile financial services are transforming the economics of international development. What really captured our attention was the realization that mobile phones are merely a conduit to the larger experience of electronic transactions, which include mobile money, but also the full gamut of wealth that is created, stored, and exchanged digitally.
Please join us for the next Technology Salon
Better than Cash
First let us agree that electronic payments systems (bank accounts, Electronic Funds Transfer (EFT), pre-paid cards, smart cards, mobile money) are a great benefit for everyone involved. Electronic payments systems:
- Increase access to basic financial services, including savings, lending, and e-payments.
- Reduce barriers to entry for fee-for-service business models
- Reduce the risk of money theft and increase personal control over financial resources
- Increase speed of payments both to and from consumers, businesses, and government
- Improve transparency, mitigate corruption, and reduce leakages in the disbursement of government funds.
A great example of all five of these benefits is the ability to pay for municipal water and electricity services via mobile money in multiple African markets. By making payments electronically, both consumers and government have more accurate records, consumers are able to save for and manage payments, and service providers can expand services with a higher expectation of payment, and more timely payment, therefore serving more customers, more efficiently.
In their Better than Cash program, USAID’s new Mobile Solutions Office seeks to expand electronic payment system use by governments, for utilities but also government payments in everything from conditional payments (welfare, healthcare, etc) for citizens, to payroll payments for government workers, to pension payments for retirees.
The net effect of this shift to electronic payments will be much more efficient government programs. Yet the Mobile Solutions team isn’t stopping with other governments, its goal is to transform the way USAID does it’s programming as well. With language already in RFP’s to encourage implementing partners to use electronic payments in their work, USAID will be pushing a move from cash payments to electronic payments for all its beneficiaries.
Barriers to Adoption
Before we get too far around the hype cycle, there are issues that will retard the growth of mobile financial services and the larger electronic payment systems. First, policy makers may have a grasp of what works to encourage electronic payments and use mobile financial services first-hand, but they don’t often know how to steer their countries from the theoretical to the practical.
Next, at the business level monopoly mobile operators may be just as hard to convince to innovate as a highly competitive mobile phone marketplace with multiple players. Neither situation lends itself to interoperability, which is key for large-scale electronic payment systems and the mobile financial services they support.
Finally, not everyone has a mobile phone. Yes, shocking but true. So simpler systems like scratch cards and offline intermediaries will co-exist with electronic payment systems for years to come. Better that we recognize and welcome them than limit any payment system to one hardware delivery mechanism, no matter its revolutionary benefits.
You are not watching this post, click to start watching









































