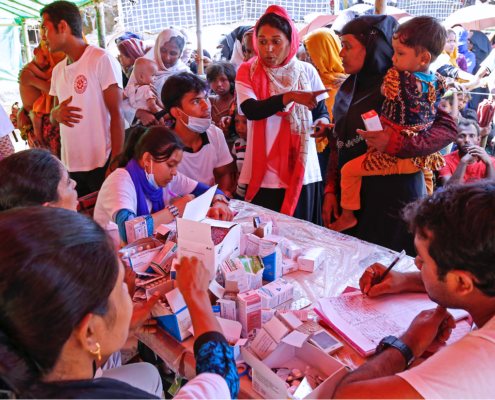
Photo Credit: AMIS-Cameroon
AMIS-Cameroon is bridging information gap in the African country of Cameroon by connecting farmers with vital information through SMS thereby boosting sustainable agricultural activities that promote the UN’s Millennium Development Goals 1 (Eradicate Extreme Poverty and Hunger), 3 (Promote Gender Equality and Empower Women), 7 (Ensure environmental Sustainability), and 8 (Develop a Global Partnership for Development).
AMIS-Cameroon uses information and communication technologies (ICTs) to create connections between farmers and agricultural technicians to encourage them to support each other through mutual advice and knowledge sharing. Through information hubs that are located in the rural farming communities, AMIS-Cameroon gathers product information and send via SMS to consumer groups who buy at farmers’ prices.
The project is using a fully coded, fully automated 24/7 information feedback loop which farmers and consumers can consult for their different needs. The concept has undergone a thorough field investigation sponsored by SPIDER.ORG and currently seeking financial support to carry out a massive outreach that would enable scaling to serve the over 12 million Cameroonian farmers. The model is simple and is replicable.
GBI followed up with AMIS-Cameroon to understand how such a simple SMS innovation can help address the United Nations Millennium Development Goals 1, 3, 7 and 8. Below is the response from Tambe Harry Agbor, the Executive Director of Amis-Cameroon.

Photo Credit: UN MDGs
AMIS-Cameroon and MDG 1: Eradicate Extreme Poverty and Hunger
The problem of Cameroonian farmers is a small reflection of what African farmers in general suffer from – acute lack of information. This lack of information means that from planting, to harvesting through location of markets to sell their products, farmers are not expose to information that predisposes them to carry out informed investment decisions to create wealth for them and their families. Given that the shelf-life of most of these agricultural products is very short, any unsold products end up as waste within the immediate vicinity of the farming population, since they do not have information about far flung markets where their products are in demand for a better price. Thus both farmers and consumers remain confined to a vicious cycle of poverty (for the farmers-since they cannot sell their products to create wealth) and hunger (for the consumers-who do not get these products which the farmers dump or give to animals)
At AMIS-Cameroon, we use SMS technology to target these alienated groups with information that brings them together in a mutually beneficial relationship where farmers can sell their products profitably and use the money to take care of life’s basic necessities such as the health and education of their children on the one hand, and on the other hand the consumers get information about where to locate nutritive products which can keep starvation and hunger at bay.
AMIS-Cameroon and MDG 3: Promote Gender Equality and Empower Women
AMIS-Cameroon democratizes the process of information dissemination. Most of our cultural values in Africa relegate women to the role of passive observer even if it is “she” who has the ideas that would take her family out of the stigma of poverty. Thus when we send the same information to both men and women, informing them how to plant crops formerly reserved for males, we are in effect giving both groups the impartial possibility to make use of the information at their disposal to best advantage. Some women farmers have till date not been able to carry out the production of certain food crops which are considered crops for men.
Furthermore, the possibility to earn stable incomes from agriculture has caused some parents to rethink their position on girl child education. When the family is poor, everything is done to make sure that the girl child stays at home and work so that her brother can get an education. But when we send out information which has the ability to connect farmers to markets, and increase the revenue streams of the family, parents then tend to feel more comfortable to invest also in the education of their girl child. Hence educated women can also vie for public office based on the possibility of their families to crawl out of the $2 per day curse to earning higher income returns that prioritizes girls’ education on the same level with boys’ education.
AMIS-Cameroon and MDG 7: Ensure environmental Sustainability
For the past decades, farmers have essentially been farming in the dark. Through ignorance, they have continued to deplete irreplaceable ecosystems and damaging the essential web of life so central to our very existence. It is not uncommon in most Cameroonian villages today for families to walk for very long distances before getting wood to cook their food, or even fauna to spice their delicacies. The fast encroaching desertification in most of our Sub-Saharan countries is a testimony of the extensive damage done to the environment through irresponsible farming practices where whole forests are destroyed, soil-enriching microorganisms killed, and loosed sub soils washed away by erosion.
In collaboration with sustainability experts and agronomists, we deliver timely advice via SMS to new entrants into the farming profession so that they can carry out responsible practices that preserve the fragile ecosystems which have been stretched to their limits by centuries of uncontrolled practices that harm none other than the farmers themselves.
AMIS-Cameroon and MDG 8: Develop a Global Partnership for Development
When we started the AMIS-Cameroon Project, one of the most recurrent complaints we encountered in the field was that experienced farmers have always refused to share their know-how with younger inexperienced farmers. We instituted an information exchange forum for farmers whereby farmers in region A tell us what must be done for a particular crop in order to enhance its productivity. When we visit Region B we shared this information with them, and those in Region B in turn become more willing to share their own experiences which we take back to farmers in region A. Through this practice we got farmers to understand that they are winners when they share agricultural technologies with one another, and that they stand to lose everything if they hide their knowledge. By encouraging them to ‘Think Development locally’ we let them see just how possible it is for them to ‘Develop Globally’.
Through our portal at www.amis-cameroon.org, we receive product requests for farmers in Cameroon from consumers from abroad. We then blast such SMS locally and farmers are rallied at short notice to supply their nearest product depot where our chain of organized transporters pick them up and deliver for onward delivery to clients.
Impacts of AMIS-Cameroon
In conclusion, AMIS-Cameroon has developed 10 business models which if sponsored shall generate direct employment and create sure revenue streams for all actors involved along the value chain. Some of the significant achievements of the project so far include increased in subscriber base from an initial 200 farmers in 2009 to well over 1500 by 2010 by providing 4 SMS per week to these users. In 2011, bee farmers in Kumbo village in Cameroon were connected to new markets enabling them to increase their sales by over 50% in markets that knew nothing about their natural honey. The project has also created a very important partnership with KIP Solutions, a firm based in the USA that is helping to define better strategies to further the vision of the project.
For more information and to support this vision of bridging information gap for African farmers, visit AMIS-Cameroon.
 Per traffic map for the recent Kony 2012 video, Chad (and Western Sahara) severely lag in broadband capacity. {YouTube}
Per traffic map for the recent Kony 2012 video, Chad (and Western Sahara) severely lag in broadband capacity. {YouTube}
![]()









































