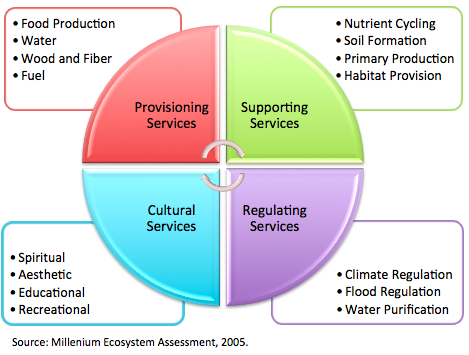
According to the Millennium Ecosystem Assessment, ecosystem services are defined as the benefits people obtain from ecosystems, split into four categories of provisioning, supporting, regulating and cultural services. Because they are so beneficial in a variety of ways, the international community has begun to monitor and monetize these services, in addition to advocating for environmental sustainability.
Each category of ecosystem services provides a certain type of benefit to the global population.
- Provisioning services are often described as ecosystem goods, and refer to benefits such as food production.
- Supporting services are services that enable other categories to work, including but not limited to nutrient production and habitat provision.
- Regulatory services, such as carbon storing, are processes often considered to be public goods, and are perhaps the most difficult to measure.
- Lastly; cultural services refer to social aspects of the ecosystem, such as the services sacred land provides and eco-tourism.
As climate change increasingly warrants international attention, a system that measures and monitors the benefits of ecosystem services will prove to be more necessary than ever before. In addition to having a set measurable indicators, it will also be valuable to monetize these services for both the public and private sector. Fortunately, some of the information and technology needed to perform these functions are already in development. The US Department of Agriculture for example, recently launched Comet 2.0, a web-based tool to help farmers estimate farm-specific carbon sequestrations and net greenhouse gas emissions from soils, biomass, annual crops, and fossil fuel usage. Another tool, the i-Tree, allows municipalities to monetize the value of urban trees, and is used in over 6,000 communities worldwide for city planning initiatives.
Recognizing the monetary value of ecosystem services, the private sector has also begun to show their commitment to the environment as part of an overall business strategy. This past June at the Rio+20 Summit, 24 global Fortune 500 companies including Coca-Cola, Dell, General Motors and Xerox, released a report called The New Business Imperative: Valuing Natural Capital. The report, sponsored by the Corporate Eco Forum and The Nature Conservancy, urges businesses to recognize how their companies are dependent on ecosystem services in a range of areas, from supply chain to cost savings. Complete with a commitment from each company involved, the report estimated the world’s ecosystem contributes about $72 trillion in goods and services per year to the global economy.
While ecosystem services may be a relatively new topic on the environmental agenda, the momentum behind the discussion is building. In fact in February 2012, the UN Statistical Commission recently approved the System for Environmental-Economic Accounts (SEEA) to account for material natural resources in a nation’s economy. It should be noted however, that an internationally accepted method of accounting for ecosystem services, as opposed to goods and materials, does not currently exist.
Because this is an increasingly important topic with a potential impact on Environmental Natural Resource Management (ENRM), we’ll be taking an in-depth look at ecosystem services in the areas of disaster risk reduction, food security, health and technology. Each week, we’ll look at specific areas of ecosystem services and how they fit into the larger development picture.